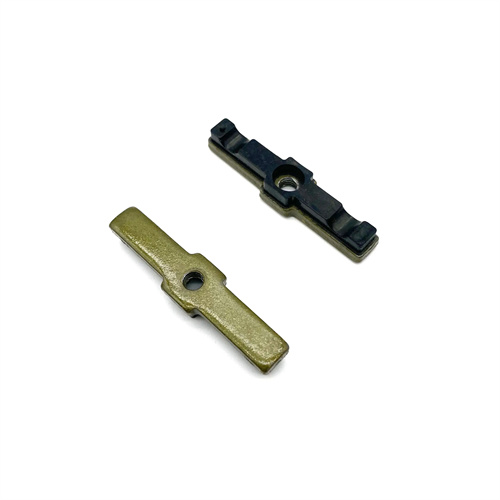
Custom OEM High Speed Stamping Stainless Steel Stamping Metal Parts
There are significant differences between high-speed stamping and regular stamping in multiple aspects, which are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Speed: The working speed of high-speed stamping is very fast, and the number of impacts per minute can reach hundreds or even thousands. Imported high-speed punching machines can even reach more than 1000 times. The speed of a regular punch is relatively slow, usually less than 200 times per minute. This high-speed impact can cause plastic deformation of metal materials in a very short period of time, completing the forming process of products.
2. Precision: High speed stamping requires higher precision. Through precise stamping die design and stable stamping process control, high consistency in product size, shape, and position can be achieved to meet high-precision requirements in product manufacturing. However, the accuracy requirements of ordinary punching machines are relatively low.
3. Scope of application: Ordinary punching machines are suitable for cold stamping processes such as forming, cutting, punching, and bending, and are widely used in industries such as electronic components, instruments, toys, automobiles, and tractors. High speed stamping is more suitable for stamping small precision parts such as precision electronics, communication, computers, household appliances, automotive components, motor stator and rotor.

4. Configuration and control: The configuration and control range of ordinary punching machines is wide, ranging from ordinary to high-end. High speed punching machines, on the other hand, are mainly equipped with high-end and CNC technology, and some are also specifically equipped with dynamic balance and balance pads to achieve more stable and accurate stamping operations.
5. Price: Due to the higher configuration and stricter precision requirements of high-speed punching machines, their prices are usually much higher than ordinary punching machines.
There are significant differences between high-speed stamping and ordinary stamping in terms of speed, accuracy, applicability, configuration and handling, as well as price. The choice of stamping method needs to be comprehensively considered based on specific production needs, material characteristics, and budget factors.
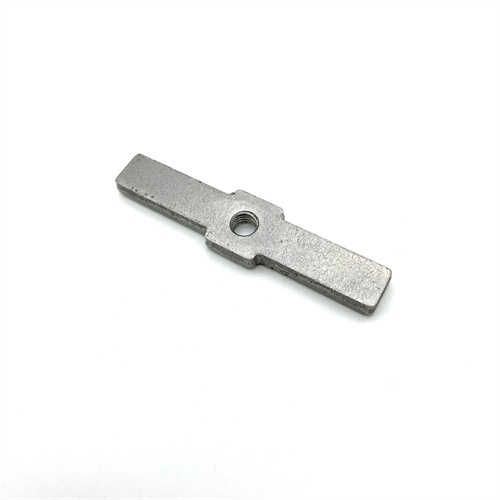

When it comes to the world of stamping, we understand that the choice between high speed stamping and regular stamping can significantly impact the outcome of a manufacturing project. While both techniques share the fundamental principle of shaping materials through the application of force, they diverge in several key aspects that are crucial for us to consider when determining the most suitable method for our clients’ needs.
One of the most immediate and noticeable differences lies in the production speed. As the name suggests, high speed stamping is engineered to operate at a far greater pace than regular stamping. Our high speed stamping presses are equipped with advanced mechanisms and powerful motors that enable them to complete a significantly larger number of stamping cycles per minute. This rapid production rate is a game-changer, especially for large-scale manufacturing projects where high volumes of parts are required in a short timeframe. For instance, in the automotive industry, where thousands of identical components need to be produced daily to keep assembly lines running smoothly, high speed stamping allows us to meet these demanding production schedules with ease. In contrast, regular stamping operates at a more moderate speed, which is better suited for smaller production runs, prototyping, or when a more deliberate and controlled approach is needed for complex designs.
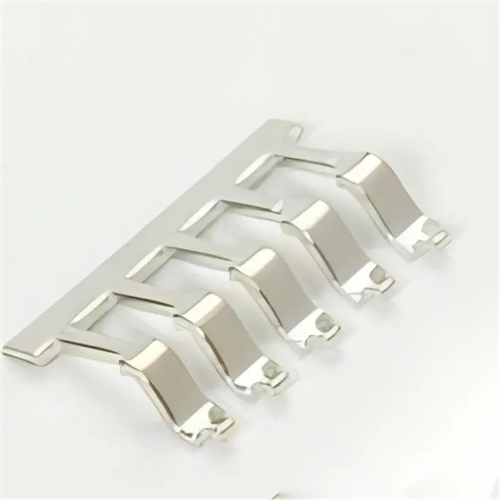

Precision is another area where these two stamping methods differ. High speed stamping, despite its rapid operation, has made remarkable advancements in maintaining high levels of precision. Our modern high speed stamping equipment utilizes state-of-the-art control systems and high-precision dies. These systems can accurately monitor and adjust the stamping process in real-time, ensuring that each part is produced with minimal variation from the desired specifications. However, due to the sheer speed, there is a marginally higher risk of minor errors if not properly managed. Regular stamping, on the other hand, offers us more time to fine-tune the process and make adjustments. This slower pace allows for a more meticulous approach, which can be advantageous when producing parts with extremely tight tolerances or intricate details that require a high degree of manual oversight and adjustment.
The cost implications of high speed stamping and regular stamping also vary. High speed stamping typically requires a significant upfront investment in specialized high speed presses, advanced tooling, and automation systems. However, in high-volume production scenarios, the economies of scale come into play. The ability to produce a large number of parts in a short time reduces the per-unit production cost significantly. Additionally, the reduced labor costs associated with automated high speed stamping contribute to long-term savings. Regular stamping, with its more basic equipment requirements, has a lower initial investment. It is often more cost-effective for small production runs or when frequent design changes are expected, as the lower setup costs make it easier to adapt to new projects.
Flexibility is another factor that sets these two methods apart. Regular stamping offers us greater flexibility in terms of handling a wide variety of materials, shapes, and sizes. The slower pace allows for easier changes in the stamping process, such as adjusting the pressure, speed, or die configuration. This makes it ideal for custom projects or when working with materials that require special handling. High speed stamping, while highly efficient for standardized parts, is more limited in its flexibility. Changing the setup for a different part design on a high speed stamping press can be time-consuming and complex, as it often involves precise calibration of multiple automated systems.
In conclusion, high speed stamping and regular stamping each have their own unique advantages and are best suited for different manufacturing scenarios. We carefully evaluate our clients’ project requirements, including production volume, precision needs, cost constraints, and flexibility demands, to determine which stamping method will deliver the best results. By understanding these differences, we can make informed decisions that optimize the manufacturing process and ensure the successful production of high-quality parts.
